GDAL+Python+Docker匹配图像范围
基础镜像
pull andrejreznik/python-gdal
编写Dockerfile文件
# 配置环境
FROM andrejreznik/python-gdal
# 工作目录
WORKDIR ./GDAL_Docker-Clip
# 从本来的路径拷贝到容器指定路径,这么写最省事
ADD . .
# 配置python环境库
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/
# 启动后台服务 #0不限制超时时间
ENTRYPOINT gunicorn run_predict:app -c gunicorn.conf.py
算法
py
#https://appliedmachinelearning.wordpress.com/2017/11/25/unsupervised-changed-detection-in-multi-temporal-satellite-images-using-pca-k-means-python-code/
from cgitb import reset
# from crypt import methods
from email.mime import image
from flask import Flask
from flask import request
from flask import Response,send_file,jsonify
from PIL import Image
import base64
import io
from flask import render_template
from werkzeug.utils import secure_filename
# 从别的文件里引用,实例化一个类,方便下面调用
# from src import yingzhibiao_predict
# p = yingzhibiao_predict.predictt()
from uuid import uuid4
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
app = Flask(__name__)
import cv2
import numpy as np
from numpy import (amin, amax, ravel, asarray, arange, ones, newaxis,
transpose, iscomplexobj, uint8, issubdtype, array)
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from collections import Counter
# from scipy.misc import imread , imresize, imsave
import imageio
# from imageio import imread
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import sys
from osgeo import gdal
from osgeo import osr
import numpy as np
from osgeo import gdalconst
# from gdalconst import *
# from osr import SpatialReference
@app.route('/', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def index():
return render_template('test.html')
@app.route('/cliptif', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def cliptif():
# data = request.form
# print(data)
# imagepath1 = request.files['img1']
# imagepath2 = request.files['img2']
# tmp_fname1 = os.path.join('Caching', uuid4().__str__()+'.tif')#?????
# tmp_fname2 = os.path.join('Caching', uuid4().__str__()+'.tif')
# imagepath1.save(tmp_fname1)
# imagepath2.save(tmp_fname2)
# print('Operating')
# 来获取多个上传文件
in1 = request.files['img1']
in2 = request.files['img2']
filename1 = secure_filename(in1.filename)
print(filename1)
in1.save(os.path.join("Caching", filename1))
filename2 = secure_filename(in2.filename)
print(filename2)
in2.save(os.path.join("Caching", filename2))
# imageio.imwrite("./Results/t1.tif", "./Caching/"+filename1)
# imageio.imwrite("./Results/t2.tif", "./Caching/"+filename2)
# msg = "http://127.0.0.1:5006/images/{}".format(filename)
# urls.append(msg)
# respose = {
# "code": 200,
# "urls": urls
# }
# return jsonify(respose)
args = [
"./Caching/"+filename1,
"./Caching/"+filename2,
"./Results/out1.tif",
"./Results/out2.tif",
"5"
]
if len(args)!=5:
print("Invalid parameters.")
print("Please input:")
print("Input path of raster 1")
print("Input path of raster 2")
print("Output path of raster 1")
print("Output path of raster 2")
sys.exit(1)
print ('参数个数为:', len(args), '个参数。')
print ('参数列表:', str(args))
#input
in_raster1 = args[0]
in_raster2 = args[1]
out_raster1 = args[2]
out_raster2 = args[3]
#read raster1---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ds1 = gdal.Open(in_raster1,gdal.GA_ReadOnly)
if ds1 is None:
print ('cannot open ',in_raster1)
sys.exit(1)
gt1 = ds1.GetGeoTransform()
proj1 = ds1.GetProjection()#获取投影信息
# r1 has left, top, right, bottom of dataset's bounds in geospatial coordinates.
r1 = [gt1[0], gt1[3], gt1[0] + (gt1[1] * ds1.RasterXSize), gt1[3] + (gt1[5] * ds1.RasterYSize)]
#read raster2------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ds2 = gdal.Open(in_raster2,gdal.GA_ReadOnly)
if ds2 is None:
print ('cannot open ',in_raster2)
sys.exit(1)
gt2 = ds2.GetGeoTransform()
proj2 = ds2.GetProjection()#获取投影信息
# r2 has left, top, right, bottom of dataset's bounds in geospatial coordinates.
r2 = [gt2[0], gt2[3], gt2[0] + (gt2[1] * ds2.RasterXSize), gt2[3] + (gt2[5] * ds2.RasterYSize)]
#calculate the intersection area of r1 and r2
intersection = [max(r1[0], r2[0]), min(r1[1], r2[1]), min(r1[2], r2[2]), max(r1[3], r2[3])]
#map intersection to pixel intersection
intersection_pixel_r1 = [geo2imagexy(ds1, intersection[0], intersection[1]), geo2imagexy(ds1, intersection[2], intersection[3])]
intersection_pixel_r2 = [geo2imagexy(ds2, intersection[0], intersection[1]), geo2imagexy(ds2, intersection[2], intersection[3])]
#read block data
clip_r1 = ds1.ReadAsArray(int(intersection_pixel_r1[0][0]), int(intersection_pixel_r1[0][1]), int(intersection_pixel_r1[1][0])-int(intersection_pixel_r1[0][0]), int(intersection_pixel_r1[1][1])-int(intersection_pixel_r1[0][1]))
clip_r2 = ds2.ReadAsArray(int(intersection_pixel_r2[0][0]), int(intersection_pixel_r2[0][1]), int(intersection_pixel_r2[1][0])-int(intersection_pixel_r2[0][0]), int(intersection_pixel_r2[1][1])-int(intersection_pixel_r2[0][1]))
#output clipped raster---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
gt_clip_r1 = [intersection[0], gt1[1], gt1[2], intersection[1], gt1[4], gt1[5]]
writeTiff(clip_r1,clip_r1.shape[2],clip_r1.shape[1],clip_r1.shape[0],gt_clip_r1,proj1,out_raster1)
gt_clip_r2 = [intersection[0], gt2[1], gt2[2], intersection[1], gt2[4], gt2[5]]
writeTiff(clip_r2,clip_r2.shape[2],clip_r2.shape[1],clip_r2.shape[0],gt_clip_r2,proj2,out_raster2)
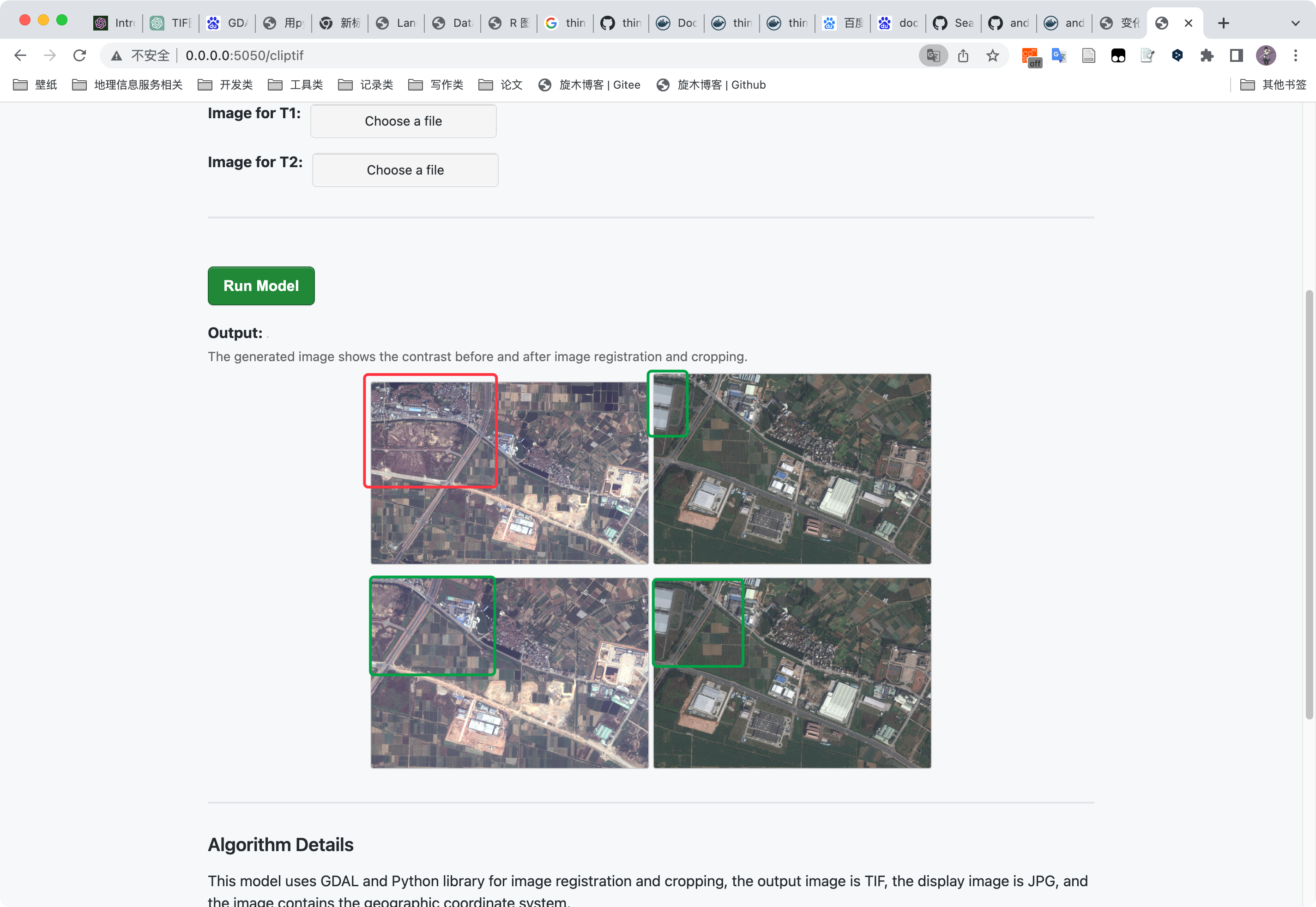
#输入t1-t2专为jpg用于显示
im1in=Image.open('Caching/'+filename1)
im2in=Image.open('Caching/'+filename2)
im1in.save('Results/in1.jpg')
im2in.save('Results/in2.jpg')
#返回显示
T1_Steam = return_img_stream("./Results/in1.jpg")
T2_Steam = return_img_stream("./Results/in2.jpg")
#输出图像转jpg用于显示
im1=Image.open('Results/out1.tif')
im2=Image.open('Results/out2.tif')
im1.save('Results/out1.jpg')
im2.save('Results/out2.jpg')
#返回显示图像
img_stream = return_img_stream("./Results/out1.jpg")
img_stream2= return_img_stream("./Results/out2.jpg")
#渲染html
return render_template('test.html',T1_Steam=T1_Steam,T2_Steam=T2_Steam,img_stream=img_stream,img_stream2=img_stream2)
def geo2imagexy(dataset, x, y):
'''
根据GDAL的六 参数模型将给定的投影或地理坐标转为影像图上坐标(行列号)
:param dataset: GDAL地理数据
:param x: 投影或地理坐标x
:param y: 投影或地理坐标y
:return: 影坐标或地理坐标(x, y)对应的影像图上行列号(row, col)
'''
trans = dataset.GetGeoTransform()
a = np.array([[trans[1], trans[2]], [trans[4], trans[5]]])
b = np.array([x - trans[0], y - trans[3]])
return np.linalg.solve(a, b) # 使用numpy的linalg.solve进行二元一次方程的求解
def writeTiff(im_data,im_width,im_height,im_bands,im_geotrans,im_proj,path):
if 'int8' in im_data.dtype.name:
datatype = gdal.GDT_Byte
elif 'int16' in im_data.dtype.name:
datatype = gdal.GDT_UInt16
else:
datatype = gdal.GDT_Float32
if len(im_data.shape) == 3:
im_bands, im_height, im_width = im_data.shape
elif len(im_data.shape) == 2:
im_data = np.array([im_data])
else:
im_bands, (im_height, im_width) = 1,im_data.shape
#创建文件
driver = gdal.GetDriverByName("GTiff")
dataset = driver.Create(path, im_width, im_height, im_bands, datatype)
if(dataset!= None):
dataset.SetGeoTransform(im_geotrans) #写入仿射变换参数
dataset.SetProjection(im_proj) #写入投影
for i in range(im_bands):
dataset.GetRasterBand(i+1).WriteArray(im_data[i, :, :])
del dataset
def return_img_stream(img_local_path):
"""
工具函数:
获取本地图片流
:param img_local_path:文件单张图片的本地绝对路径
:return: 图片流
"""
import base64
import chardet
img_stream = ''
f = open(img_local_path,'rb')
data = f.read()
print(chardet.detect(data))
with open(img_local_path, 'rb') as img_f:
img_stream = img_f.read()
img_stream = base64.b64encode(img_stream).decode()
return img_stream
# Python已经取消scipy库中imread,imresize,imsave三个函数的使用,在文件中直接写入imresize函数源代码,
def imresize(arr, size, interp='bilinear', mode=None):
im = Image.fromarray(arr, mode=mode)
ts = type(size)
if np.issubdtype(ts, np.signedinteger):
percent = size / 100.0
size = tuple((np.array(im.size)*percent).astype(int))
elif np.issubdtype(type(size), np.floating):
size = tuple((np.array(im.size)*size).astype(int))
else:
size = (size[1], size[0])
func = {'nearest': 0, 'lanczos': 1, 'bilinear': 2, 'bicubic': 3, 'cubic': 3}
imnew = im.resize(size, resample=func[interp])
return np.array(imnew)
def imread(name, flatten=False, mode=None):
"""
Read an image from a file as an array.
This function is only available if Python Imaging Library (PIL) is installed.
Parameters
----------
name : str or file object
The file name or file object to be read.
flatten : bool, optional
If True, flattens the color layers into a single gray-scale layer.
mode : str, optional
Mode to convert image to, e.g. ``'RGB'``. See the Notes for more
details.
Returns
-------
imread : ndarray
The array obtained by reading the image.
Notes
-----
`imread` uses the Python Imaging Library (PIL) to read an image.
The following notes are from the PIL documentation.
`mode` can be one of the following strings:
* 'L' (8-bit pixels, black and white)
* 'P' (8-bit pixels, mapped to any other mode using a color palette)
* 'RGB' (3x8-bit pixels, true color)
* 'RGBA' (4x8-bit pixels, true color with transparency mask)
* 'CMYK' (4x8-bit pixels, color separation)
* 'YCbCr' (3x8-bit pixels, color video format)
* 'I' (32-bit signed integer pixels)
* 'F' (32-bit floating point pixels)
PIL also provides limited support for a few special modes, including
'LA' ('L' with alpha), 'RGBX' (true color with padding) and 'RGBa'
(true color with premultiplied alpha).
When translating a color image to black and white (mode 'L', 'I' or
'F'), the library uses the ITU-R 601-2 luma transform::
L = R * 299/1000 + G * 587/1000 + B * 114/1000
When `flatten` is True, the image is converted using mode 'F'.
When `mode` is not None and `flatten` is True, the image is first
converted according to `mode`, and the result is then flattened using
mode 'F'.
"""
im = Image.open(name)
return fromimage(im, flatten=flatten, mode=mode)
def fromimage(im, flatten=False, mode=None):
"""
Return a copy of a PIL image as a numpy array.
This function is only available if Python Imaging Library (PIL) is installed.
Parameters
----------
im : PIL image
Input image.
flatten : bool
If true, convert the output to grey-scale.
mode : str, optional
Mode to convert image to, e.g. ``'RGB'``. See the Notes of the
`imread` docstring for more details.
Returns
-------
fromimage : ndarray
The different colour bands/channels are stored in the
third dimension, such that a grey-image is MxN, an
RGB-image MxNx3 and an RGBA-image MxNx4.
"""
if not Image.isImageType(im):
raise TypeError("Input is not a PIL image.")
if mode is not None:
if mode != im.mode:
im = im.convert(mode)
elif im.mode == 'P':
# Mode 'P' means there is an indexed "palette". If we leave the mode
# as 'P', then when we do `a = array(im)` below, `a` will be a 2-D
# containing the indices into the palette, and not a 3-D array
# containing the RGB or RGBA values.
if 'transparency' in im.info:
im = im.convert('RGBA')
else:
im = im.convert('RGB')
if flatten:
im = im.convert('F')
elif im.mode == '1':
# Workaround for crash in PIL. When im is 1-bit, the call array(im)
# can cause a seg. fault, or generate garbage. See
# https://github.com/scipy/scipy/issues/2138 and
# https://github.com/python-pillow/Pillow/issues/350.
#
# This converts im from a 1-bit image to an 8-bit image.
im = im.convert('L')
a = array(im)
return a
_errstr = "Mode is unknown or incompatible with input array shape."
# docker启动服务不会走main函数
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
pipreqs ./ 获取依赖
gdal 容器内已经存在 故不在这里安装
txt
chardet==5.1.0
Flask==2.2.2
numpy==1.21.5
Pillow==9.4.0
Werkzeug==2.2.2
gunicorn==20.1.0
gevent==21.12.0
构建容器
sudo docker build -t gdal_crop:v2 .
执行容器
docker run -itd -p 5050:5000 gdal_crop:v2
 旋木
旋木